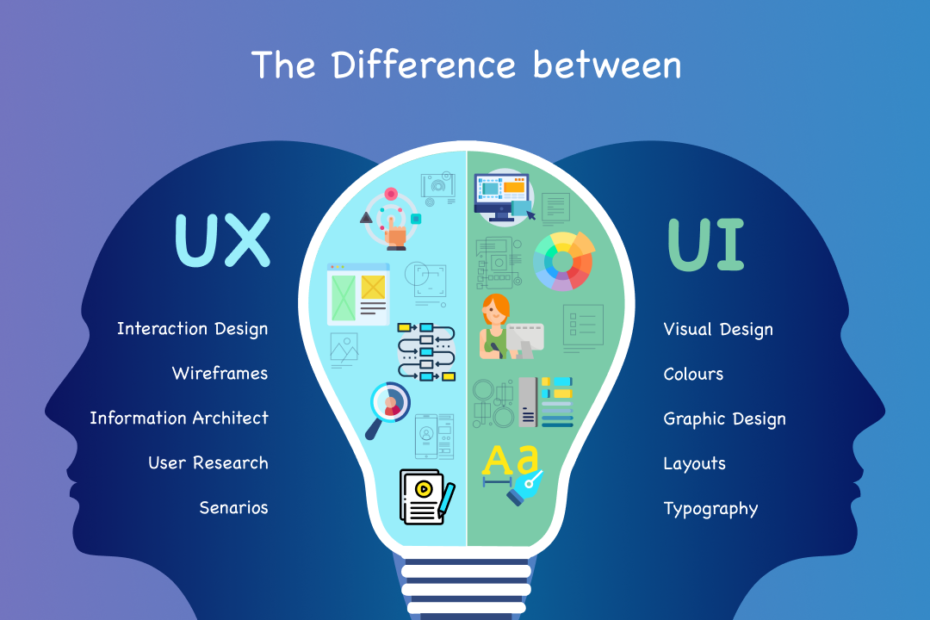
UI and UX Design are two pivotal aspects of software development, particularly in the realm of web and mobile app development. Though they are closely intertwined and often mentioned together,
UI and UX serve different purposes and encompass distinct processes in the creation of digital products. Understanding the difference between UI and UX design is crucial for developers, designers, and anyone involved in creating user centered products.
UI (User Interface) Design
UI stands for user interface. It is the point of contact between humans and computers. Any technology you interact with as a user is part of the user interface.
User interface (UI) design is the process designers use to build interfaces in software or computerized devices, focusing on looks or style. Designers aim to create interfaces which users find easy to use and pleasurable. UI design refers to graphical user interfaces and other forms.
User interfaces are the access points where users interact with designs, and it comes in three formats.
Graphical user interfaces Users interact with visual representations on digital control panels. e.g., computer’s desktop.
Voice controlled interfaces Users interact with these through their voices. Most smart assistants. e.g., Siri on iPhone and Alexa on Amazon devices.
Gesture based interfaces Users engage with 3D design spaces through bodily motions: e.g., (VR) games.

Principles of UI Design
UI design is governed by several key principles that help ensure the interface is user friendly and aesthetically pleasing:
- Clarity: The interface should be self explanatory, enabling users to understand how to interact with it without confusion.
- Consistency: Elements and patterns should be uniform across the product to help users learn and perform tasks more efficiently.
- Feedback: The design should provide feedback to users about their actions, confirming that tasks have been completed or guiding them if something goes wrong.
- Aesthetics: While functionality is crucial, the visual design also plays a significant role in creating a positive user experience. A well designed UI can enhance usability by making the experience more engaging and easier to navigate.
- Efficiency: An effective UI design streamlines tasks, making it easier for users to achieve their goals with minimum effort and in less time.
Components of UI Design
UI Design can be broken down into several components, each focusing on different aspects of the user’s interaction with the device or application:
- Visual Design: This involves the choice of color scheme, typography, and iconography that defines the look and appeal of the interface. It’s not just about aesthetics but also about communicating function and importance through visual cues.
- Interaction Design: It focuses on how users interact with the application or website, including button placement, gesture controls, animations, and overall navigation. It aims to make these interactions as intuitive as possible.
- Information Architecture: This aspect involves organizing, structuring, and labeling content in an effective and sustainable way. The goal is to help users find information and complete tasks with ease.
- Usability: While usability intersects with many areas of UI and UX design, in the context of UI, it specifically refers to making the interface understandable and easy to use.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that interfaces are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, is a critical aspect of UI design. This means considering color contrast, text size, and interaction methods that accommodate a wide range of users.
The Role of a UI Designer
A UI designer’s role is multifaceted, involving not just the creation of visually appealing designs but also ensuring that the interface is accessible, intuitive, and conducive to a great user experience. They work closely with UX designers, who focus on the overall feel of the product, as well as developers who bring these designs to life. Together, they ensure that the product meets both the aesthetic and functional needs of the user.
UI designers must stay abreast of the latest design trends and technologies to create interfaces that are not only contemporary but also future proof. They play a crucial role in the product development process, influencing how a product works and how it’s perceived by users, ultimately contributing to the success or failure of the product in the market.
UX (User Experience) Design
User Experience (UX) Design is a comprehensive approach to designing products that offer meaningful and relevant experiences to users. This process involves the design of the entire process of acquiring and integrating the product, including aspects of branding, design, usability, and function. UX Design is not just concerned with how a product looks but more importantly with how it feels to use. The goal is to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty by improving the usability, ease of use, and pleasure provided in the interaction between the customer and the product.
Principles of UX Design
The principles of User Experience (UX) Design are foundational guidelines that inform the creation of products, ensuring they are useful, usable, and desirable to users. These principles help designers focus on creating experiences that are not only functionally effective but also emotionally resonant. Understanding and applying these principles can significantly enhance the overall experience of the user, leading to products that are more engaging, intuitive, and successful in the marketplace.
1. User Centric Design
The core of UX design is a deep understanding of the users, their needs, wants, behaviors, and limitations. User centric design involves designing with the end user in mind, ensuring that their goals, contexts, and feedback are the primary focus throughout the design process.
2. Clarity
The user interface and overall experience should be straightforward and self explanatory. Every element, from navigation to content, should be clear and lead users towards their goals without confusion or ambiguity.
3. Consistency
Consistency across a product helps users learn and navigate more efficiently. This includes visual consistency (like fonts and colors), functional consistency (how elements behave), and internal consistency (maintaining the same principles and rules throughout the product).
4. Usability
Usability means making sure that something works well and that a user can perform their desired tasks without undue frustration. It encompasses simplicity, intuitiveness, and the ease with which a user can learn and use a product.
5. Accessibility
Design for all users, including those with disabilities. Accessibility involves designing products that can be used by people with a wide range of abilities, ensuring that everyone has equal access to information and functionality.
6. Minimize Cognitive Load
Cognitive load refers to the amount of mental processing power required to use the product. UX design aims to minimize this, making information easy to find and understand, thus reducing the effort users need to expend.
7. Feedback and Response Time
Providing immediate and meaningful feedback lets users know that their actions have been recognized. Additionally, optimizing response times improves the perception of the product’s reliability and responsiveness.
8. Error Prevention and Recovery
Good design anticipates possible errors and tries to prevent them. When errors do occur, providing clear, instructive, and non technical error messages allows users to recover and continue their tasks with minimal frustration.
9. Emotional Design
A product should evoke positive emotions from the user, creating a connection beyond mere functionality. This includes delight, trust, and satisfaction, ensuring that users not only achieve their goals but also enjoy the process.
10. Flexibility and Efficiency of Use
Accommodate both novice and experienced users by allowing them to tailor frequent actions to their preference. This could be through customizable shortcuts, adjustable settings, or allowing users to ‘mark as favorite’ commonly used functions.
11. Keep Users in Control
Users should feel in control of their interactions with your product. This includes easy undo and redo options, clear ways to exit undesired states, and avoiding unexpected behaviors or changes.
12. Value and Relevance
Ensure that every element provides value and relevance to the user’s task at hand. Superfluous features and information can distract from core tasks, reducing effectiveness and efficiency.
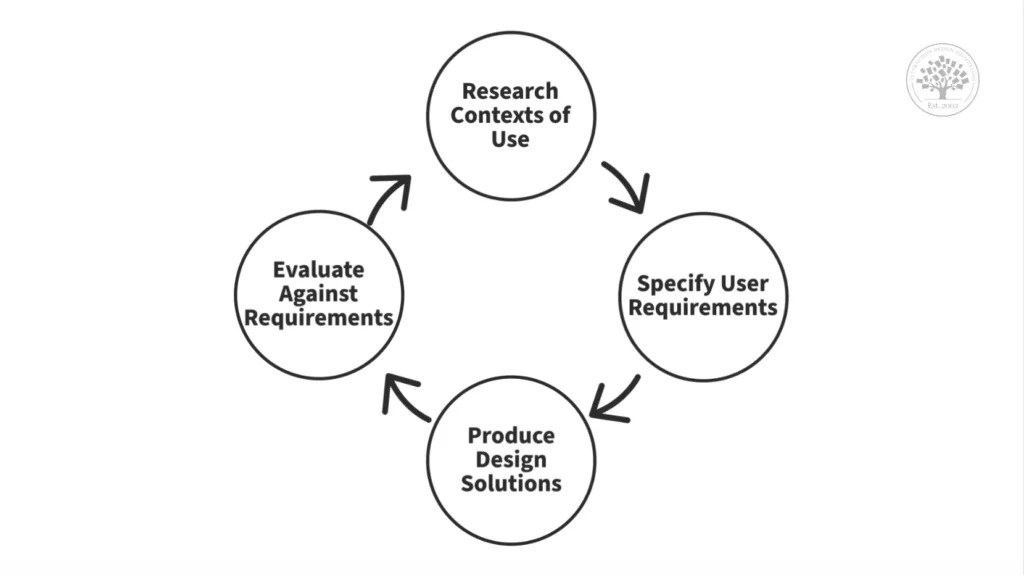
The UX Design Process
The UX design process is iterative, meaning that it cycles through stages of design, testing, and evaluation, then back again, to continuously improve and refine the product. This process typically includes the following stages:
- Research: Understanding user needs, motivations, and behaviors through interviews, surveys, and usability testing.
- Design: Developing wireframes, prototypes, and high fidelity designs that represent solutions to user needs.
- Testing: Evaluating the product by testing it with actual users to gather feedback and identify areas for improvement.
- Implementation: Working closely with developers to ensure the design is translated into a functioning product.
- Evaluation: Assessing the product’s performance and making necessary adjustments based on user feedback and business goals.
The Importance of UX Design
- User Satisfaction: A well designed user experience can lead to higher user satisfaction, which in turn can increase loyalty and user retention.
- Efficiency and Productivity: Products that are easy and pleasant to use can increase efficiency and productivity, saving time and reducing frustration.
- Accessibility: By considering the diverse needs of users, including those with disabilities, UX design helps make products accessible to a wider audience.
- Competitive Advantage: In a crowded marketplace, a superior user experience can be a significant differentiator for a product or brand.
Enozom is a software development company that plays a vital role in the digital ecosystem, specializing in creating web and mobile applications that cater to various business needs. Within Enozom, the UI/UX design role is crucial for ensuring that these applications are not only functional but also intuitive and engaging for users. UI/UX designers at Enozom are tasked with understanding user needs through comprehensive research, developing user-friendly navigation systems, and crafting aesthetically pleasing interfaces. Their work directly influences the user’s journey, aiming to enhance user satisfaction, promote engagement, and drive success for the client’s digital products. By integrating UI/UX design principles from the inception of a project, Enozom ensures that the end products are accessible, easy to use, and visually appealing, thereby aligning with the company’s commitment to delivering high-quality software solutions that meet both user expectations and business objectives.
Differences Between UI and UX Design
UI refers to the screens, buttons, toggles, icons, and other visual elements that you interact with when using a website, app, or other electronic device. UX refers to the entire interaction you have with a product, including how you feel about the interaction. While UI can certainly have an impact on UX, the two are distinct, as are the roles that designers play.
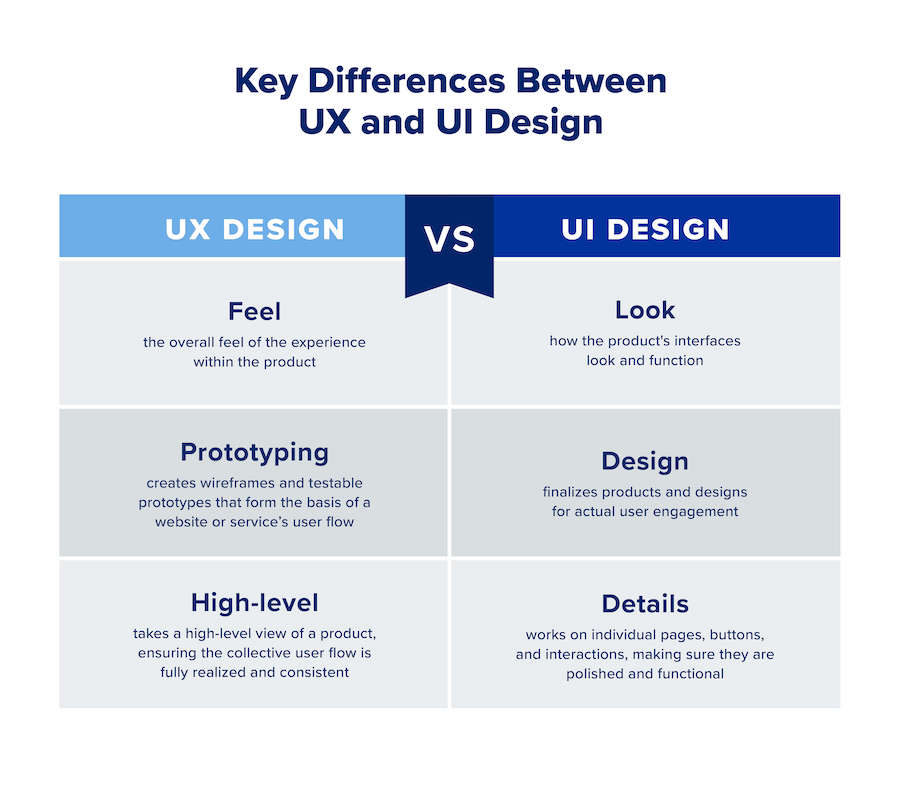
Look vs. Feel
UX and UI design play related, but different roles in a product’s development. UI design involves the look of a product namely, the visual components and interactive elements that contribute to a strong user experience. Meanwhile, UX design focuses on the overarching feel of the product or service and the components that will lead to a meaningful, relevant experience for users.
Design vs. Prototyping
UX and UI designers might work on the same product, but they have different duties and goals. UX designers often create wireframes and testable prototypes that form the basis of a website or service’s user flow, while UI designers finalize products and designs that drive user engagement.
High Level vs. Details
Another difference between UI and UX designers is the level of detail that goes into their work. UI designers work on individual pages, buttons, and interactions; making sure they are polished and functional. UX designers take a more high level view of a product or service, ensuring the collective user flow of a site, service, or app is fully realized and consistent.
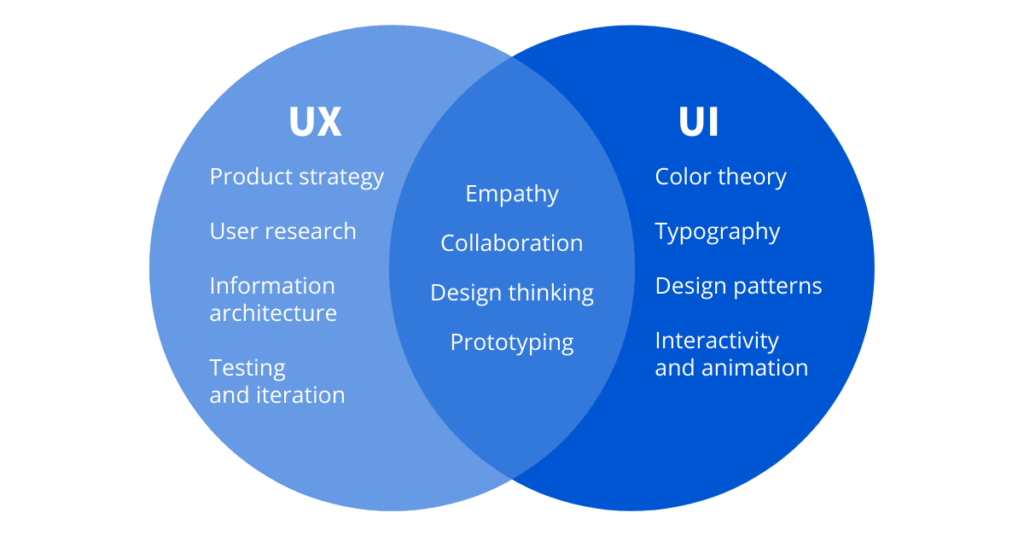
Skills
UI and UX designers have some skills in common, but each role also requires its own unique skill set.
Conclusion
UI design is a component of UX design. A comprehensive UX design strategy will consider not just how the product looks (UI), but also how it functions, how easy it is to use, and how it meets the user’s needs. Both UI and UX designers work closely together, with a shared goal of creating products that are not only beautiful but also functional, efficient, and delightful to use.
For developers and anyone involved in product creation, understanding the difference and interrelation between UI and UX design is essential. This knowledge ensures that products are not only technically sound but also provide a great experience for the end users, which is crucial for the product’s success.