Selecting the right tech stack is a crucial step in software development. It determines how efficiently your application is built, scaled, maintained, and upgraded over time. A poor choice can lead to higher costs, performance issues, or even project failure.
This guide will help you understand what a tech stack is, what factors to consider when choosing one, and explore different tech stacks used for web, mobile, enterprise, AI, and cloud-based applications.
What is a Tech Stack?
A tech stack is a combination of programming languages, frameworks, libraries, databases, frontend and backend technologies, and cloud services used to develop a software application.
It consists of two main parts:
- Frontend (Client-Side): The part users interact with directly, such as the UI and browser-based functionalities.
- Backend (Server-Side): Handles database interactions, user authentication, business logic, and server-side operations.
Additional Components in a Tech Stack
- Database: Stores and retrieves application data (e.g., PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB).
- Server & Hosting: Manages app deployment and performance (e.g., AWS, Azure, Digital Ocean).
- DevOps & CI/CD: Automates deployment and testing (e.g., Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes).
- Security Measures: Handles encryption, authentication, and compliance (e.g., OAuth, JWT, SSL/TLS).
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Tech Stack
1. Type & Complexity of the Project
The size and nature of your project dictate the best tech stack to use:
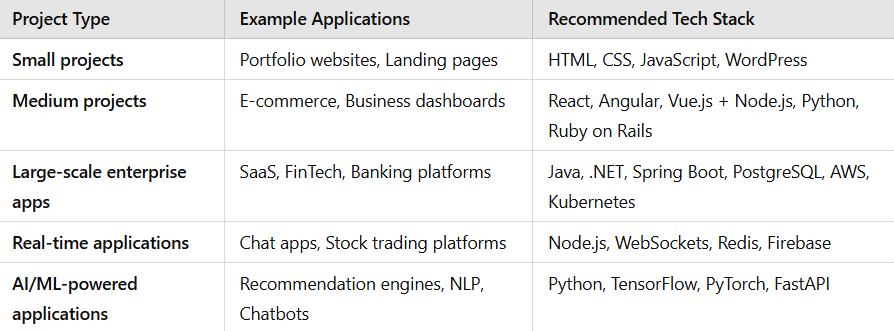
Tip: Avoid overengineering! Using a tech stack that’s too complex for a simple project may increase costs and maintenance challenges.
2. Scalability Requirements
Scalability ensures your app can handle growth in users, data, and traffic. Consider:
- Vertical Scalability: Upgrading servers for better performance.
- Horizontal Scalability: Distributing load across multiple servers.
Recommended for Scalable Applications:
- Cloud-based architectures (AWS Lambda, Kubernetes, Google Cloud Run).
- Microservices architecture (Spring Boot, Node.js, Docker).
- Scalable databases (PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Firebase, DynamoDB).
3. Development Speed & Time to Market
- Fast development frameworks like Ruby on Rails, Django, Laravel offer built-in functionalities, reducing development time.
- Low-code/no-code platforms (e.g., Bubble, OutSystems) speed up prototyping for MVPs.
If time-to-market is critical, choose a full-stack framework that allows both frontend and backend development, like:
- MERN Stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js)
- MEAN Stack (MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js)
4. Security & Compliance
Security is non-negotiable, especially for:
- Healthcare applications (HIPAA compliance)
- E-commerce and financial systems (PCI-DSS compliance)
- Data-sensitive applications (GDPR compliance)
Security Best Practices:
- Use frameworks with built-in security features (e.g., Django’s authentication system, Spring Security for Java).
- Implement encryption for sensitive data (e.g., AES encryption, SSL/TLS).
- Use authentication standards (e.g., OAuth, JWT, OpenID Connect).
5. Budget Constraints
Your budget influences your tech stack choices:
- Open-source technologies (React, Node.js, Python, MySQL) reduce licensing costs.
- Cloud-based services (AWS, Firebase) offer flexible pricing models.
- Self-hosted solutions require server maintenance costs.
Budget-Friendly Stacks:
- LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP)
- JAMstack (JavaScript, APIs, Markup) for static sites
- PaaS solutions like Heroku, Vercel, or Firebase eliminate infrastructure costs.
6. Developer Availability & Expertise
- If your team is experienced in JavaScript, a MERN or MEAN stack will be more efficient.
- Hiring developers? Python, JavaScript, and Java have larger talent pools, making recruitment easier.
Developer Market Insights (2025 Data):
- Most in-demand languages: JavaScript, Python, Java, TypeScript.
- Highest salaries: Golang, Kotlin, Rust.
- Most popular frameworks: React, Angular, Django, Spring Boot.
7. Performance & Speed Considerations
- High-performance applications (e.g., AI, gaming) require compiled languages like C++, Rust.
- Real-time applications (e.g., chat apps) benefit from Node.js + WebSockets + Redis.
- Data-heavy applications (e.g., analytics platforms) work best with Kafka, ClickHouse, Hadoop.
Popular Tech Stacks for Different Use Cases
1. Web Development Stacks
MERN Stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js)
- Use case: Startups, Single-page apps.
- Pros: Full JavaScript stack, fast rendering.
LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP)
- Use case: WordPress, CMS.
- Pros: Cost-effective, widely supported.
.NET Core (C#, ASP.NET, SQL Server)
- Use case: Enterprise apps.
- Pros: High security, Windows integration.
2. Mobile App Development Stacks
React Native + Firebase
- Pros: Cross-platform, large ecosystem.
Flutter (Dart)
- Pros: High performance, single codebase.
Swift (iOS) / Kotlin (Android)
- Pros: Native performance, best UX.
3. AI & Machine Learning Stacks
Python + TensorFlow + PostgreSQL
- Use case: AI-driven analytics, automation.
Golang + Kubernetes + Google Cloud
- Use case: Scalable AI platforms.
4. DevOps & Cloud-Based Stacks
AWS + Docker + Kubernetes
- Use case: Scalable cloud applications.
Terraform + Ansible + Jenkins
- Use case: Infrastructure as Code (IaC), CI/CD automation.
Final Decision-Making Steps
1. Define project goals – Scalability, performance, security.
2. Consider developer expertise – Pick a stack that aligns with available skills.
3. Evaluate security and compliance needs – Healthcare, finance, or SaaS.
4. Test with a prototype – Build an MVP to validate tech choices.
5. Assess long-term maintainability – Future-proof your stack to avoid migration costs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right tech stack involves balancing project needs, budget, scalability, and team expertise. Whether you select MERN for a startup, .NET for enterprise, or Python for AI, ensure that your stack supports long-term growth, security, and performance.